Wound care in home health involves the management and treatment of wounds in a patient's home, aimed at promoting healing, preventing infection, and managing any complications. This type of care is often provided by nurses, who have specialized training in wound management. It is essential for patients who have chronic wounds, post-surgical wounds, or injuries that require ongoing care and monitoring.
Key Components of Wound Care in Home Health:
1. Wound Assessment:
- Nurses evaluate the wound's size, depth, appearance, and signs of infection (e.g., redness, swelling, or discharge).
- They assess the patient's overall health and any factors that could affect healing, like diabetes or poor circulation.
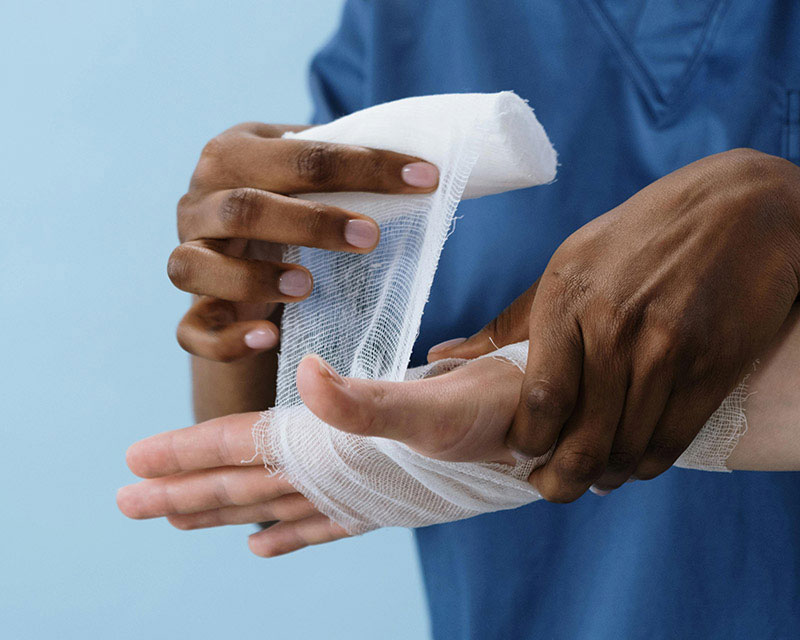
2. Cleaning and Dressing:
- The wound is cleaned with appropriate solutions to remove debris and prevent infection.
- The nurse applies a suitable dressing or bandage to protect the wound from further injury, infection, and moisture, choosing products based on the type of wound (e.g., dry, wet, or infected).
3. Infection Control:
- Nurses monitor for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or foul odor, and may take wound cultures if needed.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is detected.
4. Pain Management:
- Nurses assess pain levels and may help manage discomfort with prescribed medications or by using pain-reducing techniques during dressing changes.
5. Education:
- Nurses educate patients and their families on how to care for the wound at home, including proper cleaning techniques, when to change dressings, and signs to watch for that might require medical attention.
- They also provide guidance on preventing pressure ulcers (bedsores) or managing chronic wounds like diabetic foot ulcers.
6. Monitoring Healing:
- Nurses monitor the progress of the wound over time, adjusting the care plan if healing is slow or complications arise.
- They track the wound’s appearance and take photos or notes to document healing progress for healthcare providers.
 cottonbro studio / Pexels
cottonbro studio / Pexels
Types of Wounds Managed in Home Health:
- Chronic wounds: Such as diabetic ulcers, pressure ulcers, or venous leg ulcers.
- Post-surgical wounds: Incisions after surgery that require monitoring and care.
- Traumatic wounds: Cuts, abrasions, or burns that need treatment to prevent infection and promote healing.
In Summary:
Wound care in home health ensures that patients receive personalized treatment to manage and heal wounds while preventing complications like infections. This includes thorough wound assessments, proper cleaning and dressing, infection control, pain management, and education for patients and caregivers. Home health nurses play a key role in helping patients recover safely in the comfort of their own home.