Diabetic Management in Home Health
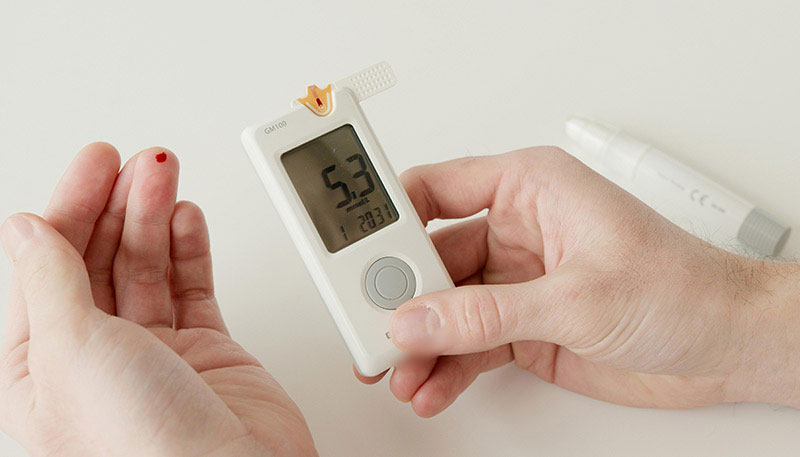
Diabetic management in home health focuses on helping individuals with diabetes manage their condition safely and effectively while living at home. This often involves a combination of monitoring blood glucose levels, managing medications, adjusting diet and exercise, and providing education and support to ensure long-term health and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
In the context of home health care, a multidisciplinary team — including nurses, physicians, dietitians, physical therapists, and sometimes social workers — work together to help patients manage their diabetes. Here are the key components of diabetic management in home health: