Physical therapy in home health involves the delivery of therapeutic exercises and treatments in a patient's home to help them recover from injury, manage chronic conditions, or improve mobility. The goal of home-based physical therapy is to enhance the patient's physical function, reduce pain, and improve quality of life while providing convenience and comfort in a familiar environment.
Key Components of Physical Therapy in Home Health:
1. Initial Assessment and Care Planning
- Comprehensive Evaluation: The physical therapist conducts an assessment of the patient’s mobility, strength, flexibility, pain levels, and overall functional abilities. This helps determine the patient's specific needs and establishes a personalized care plan.
- Setting Goals: Based on the assessment, the therapist and patient set functional goals (e.g., improving walking ability, regaining strength, or reducing pain) to guide the therapy process.
2. Therapeutic Exercises and Techniques
- Strengthening Exercises: The therapist teaches the patient exercises to improve strength in key muscle groups, particularly those weakened by injury, surgery, or chronic conditions.
- Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises: Physical therapists use stretching and mobility exercises to improve or maintain joint flexibility and prevent stiffness, which is particularly important for patients recovering from surgery or injury.
- Balance and Coordination Training: Exercises to improve balance and coordination are often incorporated, especially for elderly patients or those recovering from strokes or other neurological conditions, to reduce the risk of falls.
- Posture Training: Proper body mechanics and posture are emphasized to avoid pain and injuries in the long term.
3. Pain Management
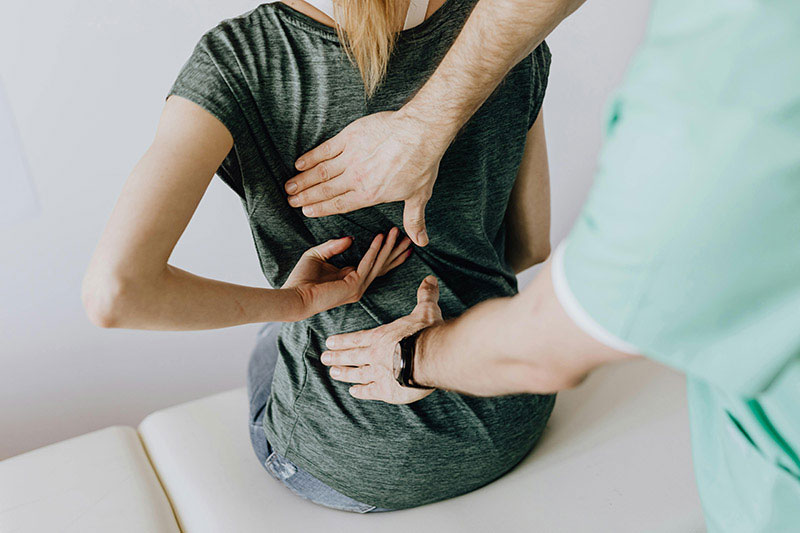
- Manual Therapy: Physical therapists use hands-on techniques like massage, joint mobilization, or soft tissue manipulation to reduce pain and increase mobility.
- Modalities: Therapists may apply heat, cold, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, or other modalities to manage pain and inflammation, helping to speed up recovery and reduce discomfort.
4. Mobility and Functional Training
- Walking and Gait Training: For patients with difficulty walking due to weakness or neurological conditions, physical therapists provide training to improve gait and coordination, often using assistive devices like walkers or canes.
- Transfers and Positioning: Therapists teach patients how to move safely, such as getting in and out of bed, chairs, or vehicles, and positioning themselves to reduce the risk of injury.
5. Home Safety and Fall Prevention
- Assessing the Home Environment: Physical therapists evaluate the home to identify fall hazards (e.g., loose rugs, inadequate lighting) and recommend modifications such as grab bars, ramps, or non-slip mats to ensure safety.
- Educating on Fall Prevention: Therapists educate patients and caregivers on techniques to improve balance and reduce the risk of falls, such as weight-shifting exercises and safe ways to move around the home.
6. Patient and Family Education
- Exercise Programs: The therapist provides the patient with a tailored exercise plan, explaining how to do the exercises safely and effectively between therapy sessions.
- Self-Management Techniques: Education on managing symptoms, improving posture, and incorporating movement into daily routines helps patients maintain progress outside of therapy sessions.
- Involving Family Members: The therapist educates caregivers and family members on how to support the patient's rehabilitation, including proper lifting techniques and helping with exercises.
7. Rehabilitation Post-Surgery or Injury
- Post-Surgical Recovery: After surgeries like hip replacements, knee surgeries, or joint replacements, physical therapy is critical for restoring movement, strength, and function.
- Injury Recovery: For patients recovering from injuries (e.g., fractures, sprains, or strains), physical therapy helps in regaining mobility and strength while minimizing pain.
8. Chronic Condition Management
- Neurological Conditions: For patients with neurological disorders like stroke, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis, physical therapy helps improve motor skills, balance, and coordination.
- Cardiopulmonary Conditions: Physical therapy is also beneficial for patients with heart or lung conditions, helping to improve endurance, strength, and overall functional ability through graded exercises.
- Arthritis and Joint Pain: Therapists work with patients to manage pain and improve joint mobility in conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other degenerative joint diseases.
Benefits of Physical Therapy in Home Health:
 Kaboompics.com / Pexels
Kaboompics.com / Pexels
Personalized Care: Therapy is tailored to the patient's specific needs, with a focus on their recovery goals and the ability to exercise and perform activities in a familiar setting.
Convenience: Patients don't have to travel to a clinic for therapy, reducing stress, travel time, and potential barriers to accessing care.
Improved Recovery: Physical therapy helps patients recover faster and more fully from surgery, injury, or illness, potentially reducing the need for hospitalizations.
Enhanced Quality of Life: By improving strength, mobility, and function, physical therapy helps patients regain independence and maintain a higher quality of life.
Fall Prevention: Patients are educated in fall prevention techniques, and the therapist may modify the home environment to make it safer, reducing the risk of injury.
Challenges of Physical Therapy in Home Health:
 Juan Manuel Montejano Lopez / Pexels
Juan Manuel Montejano Lopez / Pexels
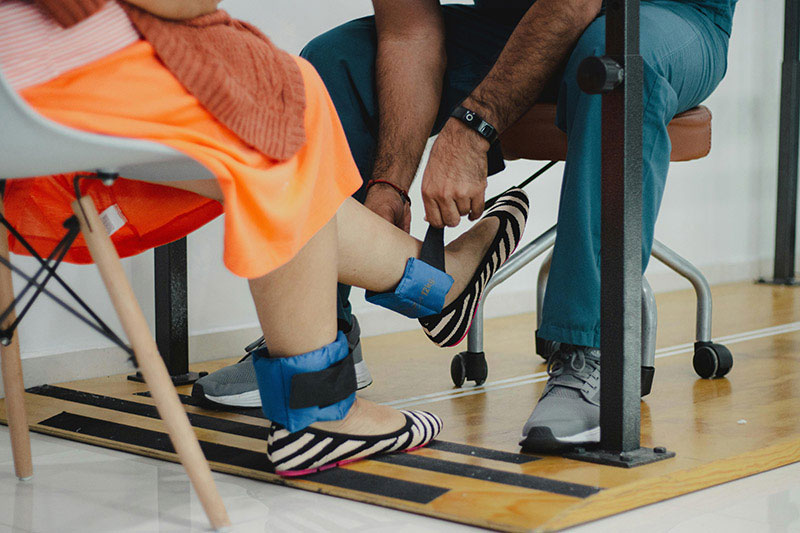
Limited Equipment: Unlike in clinics, home health physical therapy may have limited access to specialized equipment, which may limit the therapist’s ability to use certain modalities or provide more advanced exercises.
Space Constraints: Some patients may live in homes with limited space, making it challenging to perform certain exercises or activities.
Compliance and Motivation: Some patients may struggle with sticking to their prescribed exercise regimens or feel demotivated by the slow progress, making ongoing encouragement and support from the therapist essential.
In Summary
 Yan Krukau / Pexels
Yan Krukau / Pexels
Physical therapy in home health is focused on restoring and improving a patient's physical function and mobility in a familiar and comfortable environment. With personalized care, therapeutic exercises, pain management techniques, and fall prevention strategies, home health physical therapy helps individuals recover from surgery or injury, manage chronic conditions, and improve overall function and independence. By providing therapy at home, patients experience a more convenient, supportive, and personalized rehabilitation process.