Respiratory treatment in home health involves providing care to individuals with respiratory conditions or illnesses in their home environment. This type of care is typically focused on improving lung function, reducing symptoms, and improving the patient's quality of life. Home health respiratory care is essential for patients with chronic respiratory conditions such as COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), asthma, pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, or sleep apnea. It can also be part of recovery after surgery or an acute illness that impacts the lungs.
Key Components of Respiratory Treatment in Home Health:
1. Oxygen Therapy
- Indications for Oxygen Therapy: Oxygen therapy is prescribed for patients whose oxygen levels fall below normal levels, typically those with chronic lung diseases like COPD, interstitial lung disease, or severe asthma. It is also used for acute conditions such as pneumonia or after surgery.
- Delivery Methods:
- Oxygen Concentrators: These devices extract oxygen from the air and deliver it to the patient via a nasal cannula or face mask.
- Liquid Oxygen Systems: These provide oxygen in a liquid form, which can be stored in a portable tank, allowing greater mobility for patients.
- Portable Oxygen Tanks: Smaller, portable tanks are used for patients who need oxygen therapy on the go.
- Monitoring Oxygen Levels: Nurses monitor oxygen saturation levels using a pulse oximeter, ensuring that the patient is receiving an adequate amount of oxygen and adjusting the settings as necessary.
 Sincerely Media / Unsplash
Sincerely Media / Unsplash
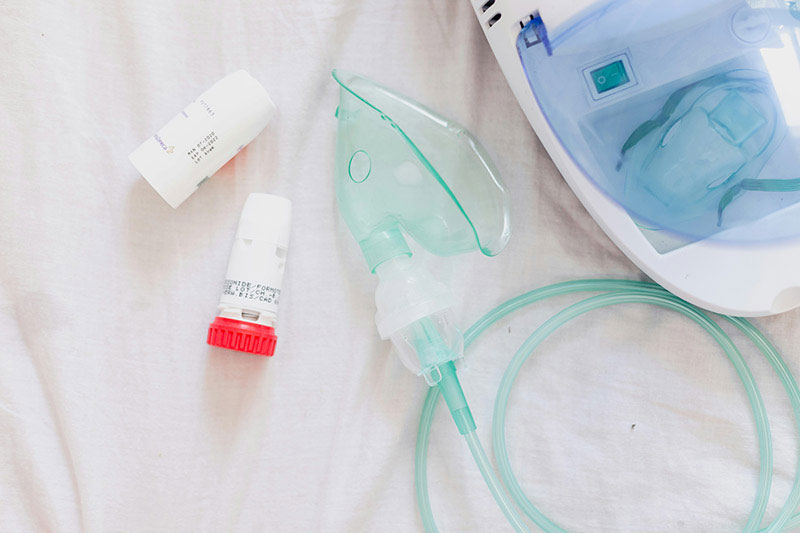
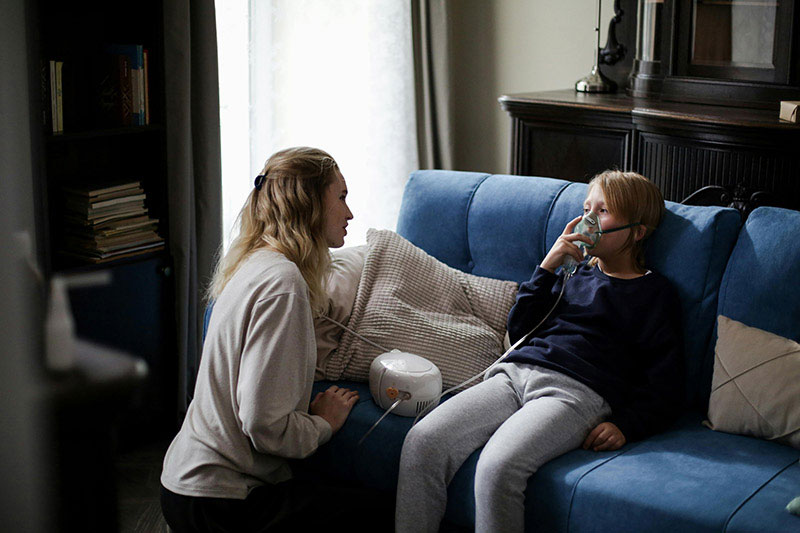
2. Nebulizer Treatments
- What is a Nebulizer?: A nebulizer is a device that turns liquid medication into a mist that can be inhaled directly into the lungs. This treatment is often used for patients with conditions like asthma, COPD, or bronchitis.
- Common Medications: Nebulized medications include bronchodilators (such as albuterol), corticosteroids, and mucolytics. These medications help open the airways, reduce inflammation, and loosen mucus.
- Administering Nebulizer Treatments: Home health nurses educate patients or caregivers on how to properly use the nebulizer machine and how to clean and maintain it to prevent infections.
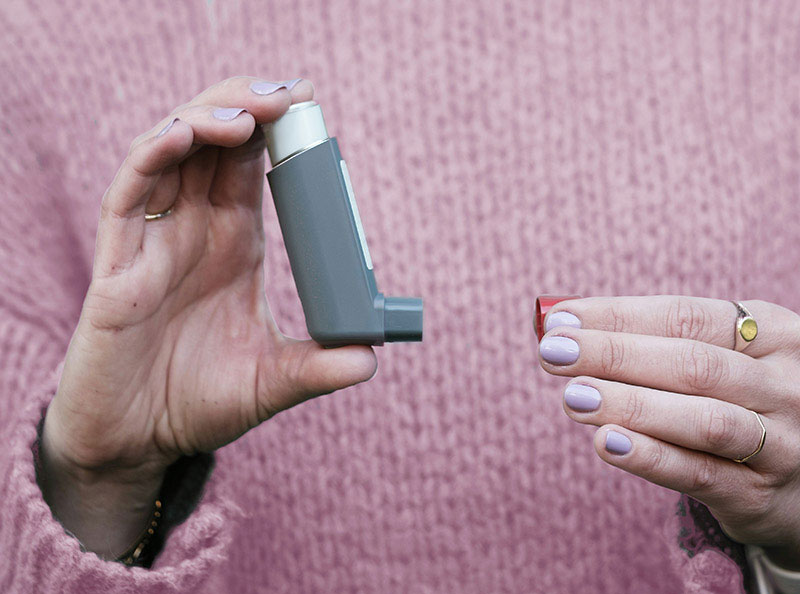
3. Inhaler Therapy
- Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs): These inhalers deliver a specific amount of medication to the lungs in a fine mist. They are often prescribed for asthma or COPD management.
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs): DPIs are another form of inhalers used to deliver medication to the lungs. They require the patient to inhale deeply to activate the powder.
- Proper Inhaler Technique: Home health nurses educate patients and caregivers on how to correctly use inhalers, including how to coordinate breathing with the inhaler to ensure effective medication delivery.
4. Chest Physiotherapy (CPT)
- Purpose of CPT: Chest physiotherapy includes a combination of techniques such as postural drainage, percussion, and vibration to help clear mucus from the lungs, which is essential for patients with chronic respiratory conditions like cystic fibrosis or COPD.
- How It’s Done: The patient may be positioned in different ways to help drain mucus from the lungs, and a therapist or caregiver will tap or vibrate the chest and back to loosen mucus.
- Self-Care Education: Patients and caregivers are educated on how to perform some of these techniques on their own at home if necessary.
5. Ventilator Care
- Indications for Ventilator Use: Some patients, especially those with severe respiratory failure, may require a mechanical ventilator to assist with breathing. These devices are more commonly used in critical care settings but can be used in the home for long-term ventilatory support in some cases.
- Ventilator Management: Home health nurses are trained to manage ventilators, adjust settings, and monitor the patient’s respiratory status.
- Patient and Caregiver Training: Training is provided to both patients and caregivers on how to use the ventilator, troubleshoot issues, and perform necessary maintenance and cleaning to prevent infections.
 KOJV / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
KOJV / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
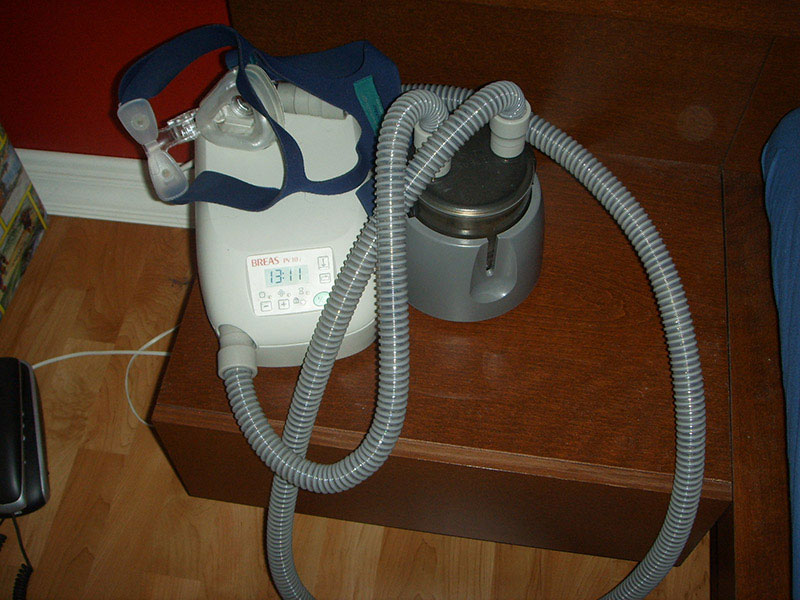
6. Positive Pressure Devices for Sleep Apnea
- CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): CPAP therapy is used to treat sleep apnea by providing a constant stream of air to keep the airways open during sleep.
- BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure): BiPAP is similar but provides two levels of pressure—higher when inhaling and lower when exhaling, often used for patients with more severe respiratory issues or conditions like COPD.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Nurses may assist in monitoring the effectiveness of the CPAP or BiPAP therapy and ensure that the device is functioning correctly. They also educate patients and caregivers on how to clean and maintain the device to reduce infection risks.
7. Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Exercise
- Purpose: Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are designed to improve lung function, enhance physical endurance, and promote overall health. Exercises and breathing techniques are often taught to strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve oxygen efficiency.
- Home Exercises: Some aspects of pulmonary rehabilitation can be done at home, with a home health nurse or physical therapist guiding the patient through exercises and breathing techniques that help improve respiratory function.
- Breathing Techniques: Patients may be taught techniques like pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing, which can help manage shortness of breath and improve oxygen exchange.
8. Education and Self-Management
- Symptom Tracking: Patients are encouraged to track their symptoms (e.g., shortness of breath, cough, sputum production) and report any changes to their healthcare provider.
- Environmental Controls: Patients with respiratory conditions are educated about avoiding triggers like smoke, dust, pollen, or pet dander that can worsen symptoms. They may also receive advice on maintaining good indoor air quality through the use of air purifiers or humidifiers.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients may be advised on lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, improving diet, staying active, and managing comorbid conditions like diabetes, which can affect respiratory health.
9. Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Regular Monitoring: Home health providers monitor the patient’s lung function and respiratory status regularly to ensure that treatments are working effectively. This includes checking oxygen saturation levels, reviewing medications, and making necessary adjustments.
- Emergency Preparedness: Nurses educate patients and caregivers about when to seek urgent or emergency care, such as signs of respiratory distress, changes in breathing patterns, or sudden worsening of symptoms.
 Sincerely Media / Unsplash
Sincerely Media / Unsplash
Benefits of Respiratory Treatment in Home Health:
- Convenience: Receiving respiratory care at home allows patients to stay in a familiar and comfortable environment while managing their condition, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
- Improved Quality of Life: Effective respiratory treatments help patients breathe more easily, manage symptoms, and prevent complications, ultimately improving their overall quality of life.
- Cost-Effective: Home health care is often more affordable than inpatient care, making it a cost-effective option for patients requiring long-term respiratory support.
- Personalized Care: Care is tailored to the individual patient’s needs, ensuring that they receive the right treatments and support for their specific condition.
 cottonbro studio / Pexels
cottonbro studio / Pexels
Risks and Challenges:
- Infection Risks: Respiratory treatments such as oxygen therapy or ventilator use can carry infection risks, so proper hygiene, monitoring, and equipment maintenance are critical.
- Patient Non-Compliance: Some patients may struggle with adhering to prescribed treatments (e.g., using CPAP or nebulizers regularly), which can impact the effectiveness of the care plan.
- Emergency Situations: Severe respiratory issues may require hospitalization or emergency intervention, and it’s important for patients and caregivers to be aware of warning signs and have a plan in place.
In Summary:
Respiratory treatment in home health focuses on helping patients manage respiratory conditions, improve lung function, and enhance their quality of life. It includes oxygen therapy, nebulizer treatments, inhalers, chest physiotherapy, ventilator management, and sleep apnea treatment, as well as education on lifestyle changes and self-care. Nurses and healthcare providers work with patients and caregivers to create tailored treatment plans, monitor progress, and ensure that the patient is receiving optimal care in the comfort of their home.